Scale Value Guide: Mastering Measurement and Analysis 2026
Master scale value with our comprehensive 2026 guide Learn precise measurement, analysis techniques, industry tools, and future trends for accurate decisions
Dec 1, 2025
published
Unlock the secrets behind accurate measurement and smarter data-driven decisions with our definitive scale value guide for 2026.
Mastering the concept of scale value is essential for anyone working with modern data, engineering, or business analysis. In this guide, we break down what scale value means, why it matters across industries, and how to use cutting-edge tools and methodologies to elevate your results.
You will discover practical steps for scaling, explore advanced analysis techniques, and get a glimpse of future trends shaping measurement in 2026. Ready to transform your approach? Dive in for actionable guidance that brings clarity and confidence to your measurement strategies.
Understanding Scale Value: Definition and Importance
Unlocking the true power of data starts with understanding scale value. This foundational concept bridges the gap between raw measurements and actionable insights in every modern field. Whether you work in science, engineering, or business, mastering scale value is key to making reliable, data-driven decisions.

What is Scale Value?
Scale value refers to the numerical representation of a measurement within a defined range or scale. It acts as the anchor for comparing values across different contexts, ensuring that data is meaningful and consistent. Unlike scaling, which adjusts data to fit a new range, or normalization, which modifies data to a standard format, scale value is about the precise point a measurement occupies.
In mathematics, engineering, and data science, scale value is used to translate real-world phenomena into quantifiable data. For example, when converting temperatures from Celsius to Fahrenheit, the scale value determines the exact corresponding figure. This precision is essential for accurate data comparison, making scale value a cornerstone of trustworthy measurement.
Why Scale Value Matters Across Industries
The importance of scale value is evident across a range of industries. In scientific research, scale value ensures that experimental results are comparable and reproducible. Manufacturing relies on it to maintain product quality and consistency. In technology, especially with IoT devices, scale value allows sensor data to be interpreted and shared accurately.
Consider IoT sensors that collect temperature or pressure data in smart factories. If the scale value is not standardized, devices may interpret the same reading differently, leading to costly miscommunications. In fact, studies show that 68% of data-driven decisions depend on standardized measurement, highlighting the critical role of scale value in maintaining data integrity and interoperability.
Common Types of Scales and Their Applications
Several types of scales are used to assign scale value, each with specific applications:
Scale Type | Description | Example Application |
|---|---|---|
Nominal | Categories, no order | Survey responses |
Ordinal | Ordered categories | Customer satisfaction |
Interval | Ordered, equal intervals | Temperature (Celsius) |
Ratio | True zero, equal intervals | Financial indices |
Selecting the appropriate scale is vital for valid analysis. Applying the wrong scale type can distort results and hamper decision-making. For a deeper dive into how measurement scales impact data analysis in fields like information retrieval, see this Measurement scales in information retrieval resource. Choosing the right scale value ensures your data is both accurate and actionable.
Challenges in Scale Value Measurement
Despite its importance, measuring scale value presents several challenges. Inconsistent data sources can introduce discrepancies, while human error and device calibration issues may skew results. For instance, when integrating legacy data into modern analytics systems, differences in scale value can compromise accuracy.
Standardization is essential to overcome these hurdles. Regular calibration and the adoption of emerging technologies, such as automated scaling solutions, are reducing errors and increasing reliability. Addressing these challenges is crucial to ensure that scale value remains a robust foundation for measurement and analysis.
The Mathematics of Scaling Values
Precise measurement starts with a strong mathematical foundation. Understanding the mathematics behind scale value is essential for anyone working with data, engineering, or analytics. This section explores core formulas, step-by-step processes, real-world examples, and common mistakes to help you master scale value calculations.
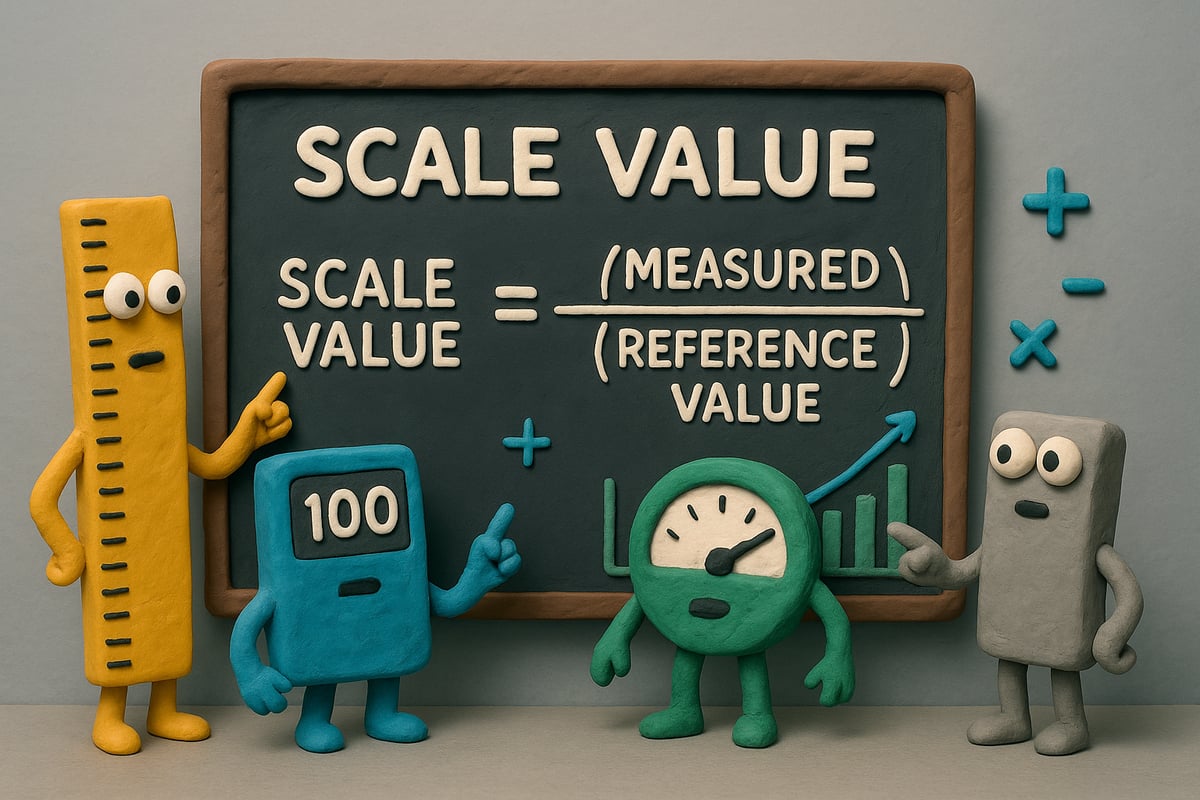
Core Scaling Formulas and Concepts
At the heart of scale value calculations lies a simple, yet powerful formula:y = y0 + (y1 y0) * (x x0) / (x1 x0)
Here’s what each variable represents:
Variable | Description |
|---|---|
x | Original value |
x0, x1 | Input range (min, max) |
y0, y1 | Output range (min, max) |
y | Scaled value |
For example, to convert a temperature from a 60 to +20 range into a 0 to 255 scale, simply plug the values into the formula. This mathematical approach ensures every scale value transformation is accurate and reliable.
Step-by-Step Scaling Process
Mastering the scale value process requires a systematic approach. Begin by identifying the input and output ranges. Adjust for any negative values to ensure consistency. Next, apply the scaling formula accurately. Finally, round or format the result to suit your application.
For instance, if you need to scale a value from 15 to 15 into a 0 to 165 range, the process is the same. Consistency in these steps prevents errors and ensures every scale value is both meaningful and actionable.
Practical Examples Across Domains
Scale value calculations are indispensable across many fields:
Hardware: Scaling sensor inputs for serial control devices.
Data science: Feature scaling to prepare datasets for machine learning.
Finance: Normalizing financial indices for comparison.
Engineering: Performing unit conversions for accurate measurements.
The universality of scale value mathematics makes it a foundational tool, enabling professionals to compare, interpret, and act on data regardless of the domain.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Errors in scale value calculations often stem from a few key oversights:
Forgetting to check input or output range boundaries.
Overlooking differences in measurement units.
Ignoring the impact of outliers or data skew.
Misinterpreting sensor readings due to uncalibrated devices.
To avoid these pitfalls, always double-check formulas, verify data sources, and ensure assumptions are documented. Careful attention at each step will safeguard the accuracy of every scale value you compute.
Tools and Technologies for Scale Value Measurement in 2026
Accurate scale value measurement depends on both innovative software and reliable hardware. In 2026, organizations are leveraging a new generation of tools to ensure precision, speed, and security in every application. Let us explore the key technologies powering scale value measurement and how they shape the future of data-driven decision-making.

Modern Software Solutions
Software platforms are the backbone of modern scale value measurement. Today’s leading solutions offer automated scaling, robust visualization, and integrated error-checking to streamline workflows. Tools like Python’s NumPy and pandas libraries allow users to apply complex scaling formulas with minimal manual effort.
Many organizations turn to specialized platforms, such as the Clayworks homepage for measurement tools, which provide user-friendly interfaces for scale value operations. These solutions are equipped with customizable dashboards, batch processing capabilities, and real-time analytics.
A key benefit of modern software is the reduction of manual scaling errors. With built-in validation and data integrity checks, teams can trust their results and focus on higher-level analysis.
Hardware and Digital Measurement Devices
Hardware advancements are transforming how scale value is captured in real time. Digital calipers, IoT sensors, and industrial controllers now come with built-in scaling and automated calibration features. These devices can instantly normalize raw data, ensuring that measurements are accurate before entering analysis pipelines.
For example, smart sensors in manufacturing environments automatically adjust for environmental factors, outputting consistent scale value data. This minimizes the risk of human error and maintains process reliability.
Integration between hardware and software is seamless, allowing for continuous monitoring and rapid feedback. The result is increased efficiency and improved measurement accuracy.
Open Source Libraries and Community Tools
Open source libraries are driving innovation in scale value processing. Projects like SCALE codec for blockchain and paritytech/scale-value offer dynamic value encoding and decoding, which are essential for secure and flexible data exchange.
Community-driven standards help organizations adopt best practices and reduce the learning curve. Many teams contribute to these tools, ensuring rapid updates and shared problem-solving.
A simple example is using an open source Python library to scale sensor data for IoT applications. This approach is cost-effective, transparent, and highly adaptable to new requirements.
Integrating Scale Value Tools in Business Workflows
Successful scale value implementation requires thoughtful integration into business processes. Start by assessing current measurement needs and identifying gaps. Next, select tools that are compatible with existing systems and scalable for future growth.
Training staff and updating protocols is essential. For instance, manufacturing firms often integrate scale value tools into quality control systems, automating data collection and analysis.
Seamless integration enhances productivity and ensures that scale value data remains reliable across departments. It also supports compliance and traceability in regulated industries.
Security and Compliance in Scale Measurement
Security and regulatory compliance are critical for scale value measurement, especially in sensitive fields such as healthcare or finance. Features like audit trails, encryption, and tamper-proof logs protect data integrity and privacy.
For example, healthcare devices must adhere to strict guidelines for measurement accuracy and record-keeping. Secure scale value tools offer built-in compliance checks and real-time monitoring.
Prioritizing security in scale value workflows not only safeguards data but also builds trust with stakeholders. As requirements evolve, organizations must stay proactive in maintaining best practices and meeting new standards.
Step-by-Step Guide: Mastering the Scaling Process
Mastering the scale value process is crucial for anyone aiming to achieve accurate, reliable measurements. This step-by-step guide ensures you can confidently navigate preparation, method selection, calculation, validation, and troubleshooting. Each phase, from data gathering to optimization, builds a foundation for trustworthy analysis and actionable insights.
Preparation: Define Objectives and Gather Data
Begin your scale value journey by clarifying your project objectives. Determine what you need to measure and the level of precision required. This step sets the stage for all subsequent work.
Next, gather all relevant raw data. Validate each data point for completeness and accuracy. For example, before analyzing survey results, confirm that responses are legible and within expected ranges.
Proper preparation prevents costly errors later. When your foundation is solid, your entire scale value process will be smoother and more reliable.
Choosing the Right Scale and Normalization Method
Selecting the appropriate scale value and normalization approach is vital. Assess your dataset's distribution, range, and the specific requirements of your analysis. Common methods include min-max scaling, z-score normalization, or custom formulas tailored to unique domains.
For instance, machine learning models often require feature scaling to ensure inputs are comparable. In some advanced fields, like psychometric analysis, researchers use neural network techniques to uncover latent dimensions, as seen in Neural network embeddings in psychometrics.
Choosing the best method directly impacts the quality of your scale value output and the insights you derive from your data.
Applying the Scaling Formula
With your method chosen, apply the scale value formula systematically:
x: original valuex0,x1: input range minimum and maximumy0,y1: output range minimum and maximum
For example, to scale -15 to 15 into 0 to 165:
Always double-check calculations. Consistency in applying the scale value formula is key to avoiding errors.
Validating and Interpreting Scaled Data
Once you've applied your scale value formula, validation is essential. Use visualization tools like scatter plots or histograms to spot anomalies and outliers. If results deviate from expected patterns, revisit your data and scaling steps.
Interpret scaled results in context. For instance, in quality assurance, plotting scaled sensor readings can reveal equipment drift or process inconsistencies. Reliable validation ensures your scale value analysis stands up to scrutiny and supports informed decisions.
Troubleshooting and Optimizing the Scaling Process
Even with careful planning, issues can arise in the scale value process. Common problems include data drift, sensor calibration loss, or the introduction of new data sources.
To address these, establish regular audits and automated alerts within your workflow. In manufacturing, real-time monitoring systems can immediately flag scaling inconsistencies, allowing quick intervention.
Continuous improvement and optimization are central to maintaining long-term accuracy and extracting maximum value from your scale value approach.
Advanced Analysis: Leveraging Scaled Data for Insights
Unlocking the full power of scale value opens doors to deeper, more actionable insights across every data-driven field. With accurate scaling, organizations move beyond raw numbers to unlock trends, patterns, and predictive power that drive real results.
Statistical Methods Post-Scaling
Applying statistical techniques to well-prepared scale value data transforms basic measurement into powerful analysis. Methods like regression, clustering, and principal component analysis (PCA) rely on properly scaled values for accuracy.
For example, scaling features before regression ensures that each variable contributes equally to the model, preventing bias toward larger numerical ranges. In clustering, scale value standardization helps algorithms identify true groupings rather than being misled by disparate units.
Ultimately, using robust scale value practices enhances the reliability of any statistical method, leading to more precise and trustworthy conclusions.
Visualization Techniques for Scaled Data
Visualization is where the impact of scale value becomes immediately clear. Tools like heatmaps, scatter plots, and interactive dashboards allow analysts to compare scaled datasets side by side, revealing trends and anomalies that might otherwise go unnoticed.
Consider how a heatmap of scaled survey responses can quickly highlight outliers or clusters. Comparing unscaled versus scaled data visualizations often shows dramatic improvements in clarity and interpretability.
By leveraging the right visualization tools, professionals can communicate scale value insights to both technical and non-technical audiences with ease.
Case Studies: Real-World Success Stories
Across industries, scaling data with the right scale value approach leads to measurable improvements. Healthcare diagnostics, financial forecasting, and IoT analytics all benefit from reduced analysis time and higher accuracy.
One compelling example is in mobile commerce, where rigorous scale value measurement has enabled businesses to better understand customer behavior. According to a study on perceived value measurement in mobile commerce, the adoption of validated scales resulted in up to a 47 percent reduction in analysis time.
These real-world cases highlight the return on investment that proper scale value application delivers.
Ethical Considerations and Bias Prevention
Ethical use of scale value is essential for trustworthy analysis. Improper scaling can introduce bias or mislead stakeholders, especially in sensitive fields like healthcare or AI.
To prevent these risks, organizations should adopt transparent scaling methodologies and conduct regular audits. For example, a systematic review of self-care scales in nursing underscores the importance of validating scale value measurements to ensure fair, accurate outcomes.
Maintaining ethical standards in scale value analysis protects both data integrity and public trust.
Future Trends in Scale Value Measurement and Analysis
The landscape of scale value measurement is evolving rapidly as technology advances. Staying ahead of these changes is essential for organizations seeking to maintain accuracy, efficiency, and compliance in their measurement and analysis workflows.
AI and Automation in Scaling
Artificial intelligence is transforming scale value workflows by automating complex scaling tasks and learning optimal calibration patterns. Modern AI algorithms can instantly detect anomalies in scaled data, reducing manual oversight and increasing response speed. For example, machine learning models can adaptively recalibrate measurement devices, ensuring the scale value remains accurate even as conditions change.
By leveraging AI-driven tools, organizations can streamline processes and minimize human error. These advancements allow for real-time adjustments, enabling systems to maintain high-quality data integrity. As AI continues to evolve, expect scale value analysis to become even more precise and reliable.
Integration with IoT and Edge Computing
The rise of IoT and edge computing is revolutionizing how scale value is measured and utilized at the data source. Smart sensors now perform real-time normalization before transmitting information, dramatically reducing latency and bandwidth requirements.
This local processing ensures that scale value data is clean and standardized as soon as it is generated. For industries like manufacturing and logistics, such improvements mean faster decision-making and reduced risk of errors. Edge computing also enhances security by limiting data exposure, making scale value measurement both efficient and safe.
Evolving Standards and Regulatory Landscape
International standards for scale value measurement are undergoing significant updates as digital transformation accelerates. Organizations must stay informed about new protocols, such as revised ISO guidelines for digital measurements, to ensure ongoing compliance.
Adopting these evolving standards helps guarantee interoperability and trust across global operations. Regulatory bodies are emphasizing transparency in scale value processes, requiring robust documentation and audit trails. Staying current with these changes is crucial for organizations that rely on precise measurement and analysis.
Preparing for 2026 and Beyond
To future-proof scale value strategies, professionals should invest in scalable, modular systems and foster cross-industry collaboration. Developing expertise in emerging tools and methodologies will be essential for adapting to rapid technological shifts.
Engaging with industry leaders and platforms is a proactive way to stay updated. For those seeking early access to the latest measurement and scaling innovations, consider joining the Clayworks waitlist for updates. By embracing continuous learning and innovation, organizations can confidently navigate the evolving world of scale value into 2026 and beyond.
Article written using RankPill.
